Notebook is a secondary storage device where data is stored as magnetic pulses on a rotating metal disc that is integrated. Data is stored in concentric circles called tracks. Each track is divided into several segments, known as sectors. To perform read and write operations to and from a data disc, hard disk using the head to do it, which is in every dish. Head is a moving look hereinafter sector-specific sector for operation against him. The time required to find a sector called seek time. After finding the desired sector, then the head will turn to look for tracks. The time required to find the track is called latency.
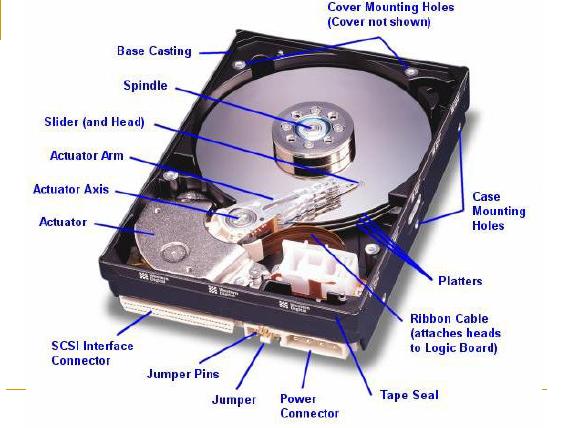
Hard drive storage is designed to be used to save the data in a large capacity. This is a background application that does not allow programs to be in one disk and also require large storage media files such as an agency database. Not only that, the hard drive is also expected to be offset from the speed of access. Hard drive speed when compared with regular floppy disks, so far. This is because hard drives have different mechanisms and materials technology are certainly better than regular floppy disks. When no hard drive, you can imagine how much that must be provided to store data of any public employee or store application programs. It's certainly not efficient. Plus a very slow reading time when using conventional disk storage media.
History of Hard Drive
Disks in early development is dominated by giant companies that became standard computer that is IBM. Good over the years emerged other companies such as Seagate, Quantum, Conner up with Hewlett Packard's in 1992. At first the technology used to read / write, the head read / wrote and metal disc penyimpannya touching. But at this time it is inevitable, due to the current disk rotation speed is high, touch the metal plate it will damage the physical storage from disk.
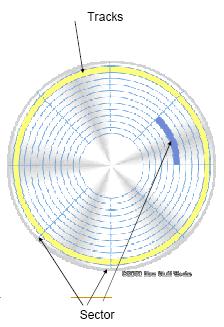
Gambar 1 : Evolusi Teknologi Hardisk Menurut IBM
From the figure it can be seen from 1984 to 2006 to come, the development of data storage technology is growing fast. Ranging in size from micro to use laptops to normal size for desktop PC use.
Disk Development Trend
Drive the development trend can be observed from the following characteristics:
a. Density Data / Technology Materials
Is a measure of the material used technology how big bits of data that can be stored in one square unit. In terms of density data from the beginning to present the evolution of highly contrasting. At the beginning of its development around 0004 Gbits/in2 kerapannya but labortorium IBM in 1999 there were about 35.3 Gbits/in2. But according www.bizspaceinfotech.com be introduced so-called TerraBit density.Harddisk in early development, the material used as the storage medium is iron oxide. But now widely used thin film media. Media is more media stores data from the iron oxide over the same area and also its more durable.
b. Structure of read / write head
Read / write heads are intermediaries between the physical media to electronic data. Through this head data is written to or read from the physical medium physical medium. Head will change the data bits to magnetic pulses and write to the physical medium. In the process of reading the data process is the opposite.
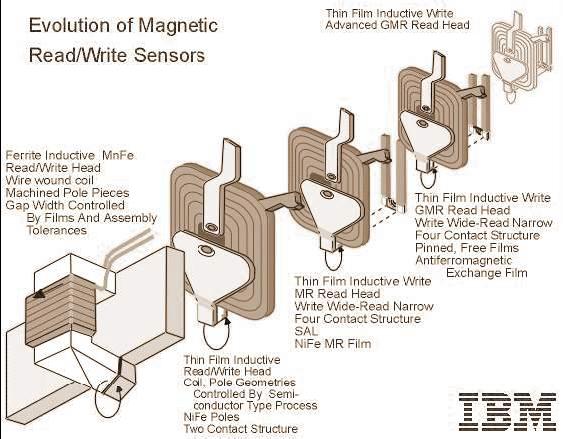
Figure 2 Design characteristics of most read / write head
The process of reading and writing of data is very important, therefore, the mechanism is also noteworthy. In a previous preliminary physical layout head there is a difference in the operation. Head first physical contact with the metal storage. Now, between the head and the metal storage already given distance. When the head is in contact with the metal storage, it will cause permanent damage to physical, head worn, of course, the heat caused by friction. Moreover, current technology disk rotation speed is very fast. Additionally harddiskpun head technology also evolves. The evolution of read / write head disk: head Ferrite, Metal-In-Gap (MIG) heads, Thin Film (TF) Head, (Anisotropic) Magnetoresistive (MR / AMR) Heads, Giant Magnetoresistive (GMR) Heads and is now being used is Colossal Magnetoresistive (CMR) Heads. Ferrite head, is the head of the most ancient technologies, the core is made of iron U-shaped and wrapped by an electromagnetic coil. This technology is implemented in mid-1980 on the Seagate ST-251 hard drive. Most are on the hard drive size is less than 50MB.Metal-In-Gap (MIG), a refinement of the head Ferrite. Typically used on hard drives the size of 50MB to 100MB. Thin Film (TF) heads, different from the kind of head before. Head is made with photolothografi processes such as those used in the manufacture of the processor. (Anisotropic) Magnetoresistive (MR / AMR) Heads, head is used for reading only. In order to use the writing head type Thin Film. Implemented on a hard drive the size of 1GB up to 30GB. Giant Magnetoresistive (GMR) Heads, an invention of European researchers Peter Gruenberg and Albert Fert. Used in large sizes such as 75GB hard drive and a high density of approximately 10 to 15 Gbits/in2 Gbits/in2.
Because the technology Giant Magnetoresistive (GMR) began to be withdrawn from the market, as a successor is Colossal Magnetoresistive (CMR).
Play Speed Disk
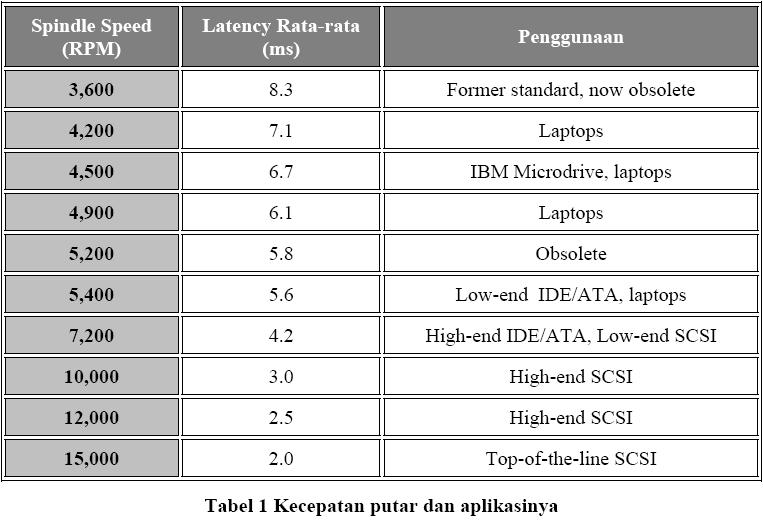
3. capacity
The capacity of the hard drive at this point has reached the order of hundreds of GB. This is because the technology is getting better materials, higher data density. Technology from Western Digital is now able to make a 200GB hard drive with 7200RPM speed. While the Maxtor Maxtor his Maxline II is a disk size of 300GB with 5400RPM speed. Along with the transition to a smaller hard drive size and the growing capacity of the dramatic decline in the price per megabyte of storage, large capacity hard drives make the price achieved by ordinary computer users.
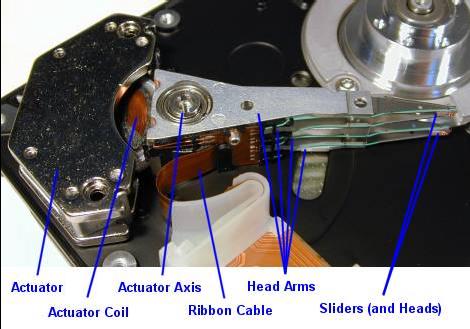
Hard Drive Technology a future
One hard drive in the future emphasis on access speed and capacity. This can be done by reducing the mechanical components of the physical hard drive. Mechanical components that are not capable of working at high frequency is shifted by the electrical components that are capable of working in order of MHz and even GHz.
Can be seen today has released a wide range of electronic media storage in a small form. For example, USB Drive and MultiMedia Card. When will this technology can be applied and affordable, computer capabilities in terms of speed of read / write storage media will increase rapidly. Automatic PC Server capabilities to service the request from the client will increase.
Here is Some Reference Summary About Hard Disk;
INTERFACE HARD DISK IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics);
old standards that still exist. Cheap, and integrated with MB is the reason this technology theta p ada.Jumlah IDE there are 4 pieces each MBKoneksi with flat cable 80 pininterface a bottleneck and impede heat
SCSI (Small Computer Standard Interface)
Speeds up to 160 mb / sec SCSI type (SCASI I, Wide SCSI, Ultra Wide) Using new technology tersendiriMB card already includes a card SCSInya.
SCSI is typically used for server systems, which demand high performance SCSI system technology, known as RAID, system preparation, writing, security with several HD.
RAID (Redundancy Array of Independent Disks), is a set DiskDrive seen by the OS as drive tunggal.Recovery and security a priority.
Hard Drive Installation
IDE cables are red strip Power supply plugged in adjacent or parallel cable with red on one computer will not IDEJika bootingLakukan detection of HD through BIOS
Process Read Hardisk
When an operating system sends data to the hard drive for recording, the drive is processing the data using a complex mathematical formula that adds an extra bit of data tersebut.Bit does not take place: In the future, when the data is retrieved, the extra bits allow drive to detect and correct errors caused by random variation of the magnetic field inside the drive. Then, the drive head moves through the appropriate track of the platter. Time to move the head is called the "seek time". While on the right track, wait until the platter spinning drive to the desired sector is under the head. The amount of time is called "drive latency". The shorter the time `seek` and `latency ', the faster the drive to complete its work. When electronic components drive determines that a head is above the appropriate sector to write data, the drive sends electrical pulses to the head. Pulse produces a magnetic field that changes the magnetic surface on the platters. Variations are now representing a recorded data. Reading data requires some recording process. Drive position the part of the reader head over the appropriate track, and then wait for the right sector to spin on it. At certain magnetic spectrum that represent your data in the sector and the right track just above head reader, electronic components drive detects small changes in the magnetic field and turn it into bits. When the drive was completed checks and corrects errors in bits if necessary, he then sends the data to the operating system.

Sectors and Tracks
Tracks are part of the circumference of a circle from the outside sepanjanjang to dalam.Sedangkan sector is part of tracks.Sectors has a number of bytes that have been set.
There are thousands sector in HD
1 sectors normally store 512 bytes of information
Notebook Makers Materials
Currently hd made with magnetic media materials technology called thin film.Lebih meeting, the battery life, small, light weight of oxide materials

Mechanism of Hard Disk
The process of reading and writing done by the media arm of Physical magnetikHead hd hard to convert bits to magnetic pulses and store it into the platters, and restore the data if the hard disk has a reading performed "Hard platter" that serves to store magnet.Pada field basically means hard work disk is to use magnetic recording technique. The workings of the magnetic technique utilizes Iron oxide (FeO) or rust of iron, Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) or other oxide of iron. 2 oxide is a substance that bersifatferromagnetic, that if brought to the magnetic field it will be permanently withdrawn by the substance.










0 komentar:
Posting Komentar